click to get service View profile
Discover what Usability Testing is and learn an effective testing process to improve user experience. Optimize your product with real user feedback and insights.
During product development, Heuristic Evaluation is a useful tool that helps the Product team identify UX bottlenecks early. However, is relying solely on design principles enough to ensure a product runs smoothly in real-world usage?
Statistics show that 43% of UX issues detected through Heuristic Evaluation are not actual usability problems. This is why UX experts often combine this method with Usability Testing, where the Product team directly observes how users interact with the product, tracks their behavior and feedback, and makes necessary adjustments accordingly.
Even Jakob Nielsen, the creator of the 10 Usability Heuristics, stated that testing with just 5 users can uncover up to 85% of usability issues.
So, what is Usability Testing? How does it help optimize the user experience? And how can it be effectively implemented? Let’s explore these questions in the article below!
What is Usability Testing?
Usability Testing is a crucial method in product design and development, used to evaluate how user-friendly and effective a product is when users interact with it. The main goal is to identify issues users face and improve the User Experience (UX) accordingly.
During the testing process, participants perform specific tasks on the product while researchers and UX designers observe, collect data, and analyze their behavior. This method focuses on:
- Evaluating users’ ability to complete tasks independently and efficiently.
- Measuring usability performance, including interaction speed, errors encountered, and emotional responses.
- Assessing user satisfaction, ease of understanding, and comfort while using the product.
- Identifying potential UX issues and proposing optimal solutions.
Through Usability Testing, the Product team can validate design decisions, enhance the user experience, and ensure the product effectively meets real user needs.
Difference Between Usability Testing and User Testing
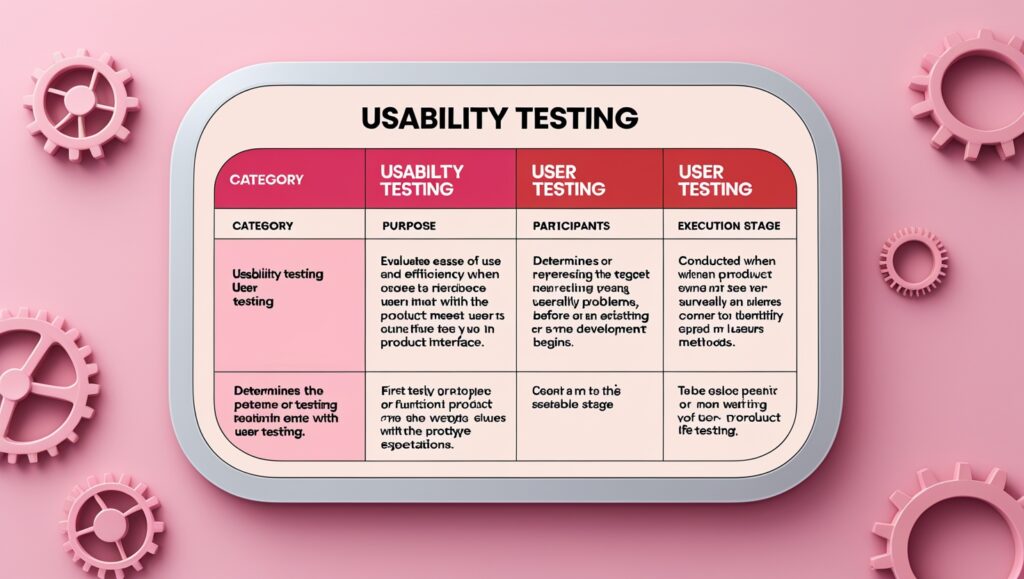
Both Usability Testing and User Testing are important approaches that help the Product team better understand users during the product design process. However, they have different objectives and are applied at different stages.
1. Main Objective
- Usability Testing focuses on the ease of use and user experience of the product. It answers the question: “Is this product intuitive, user-friendly, and effective for real users?” The goal is to optimize usability, ensuring users can complete tasks quickly and easily.
- User Testing focuses on evaluating the product’s fit with its target audience. It helps determine whether the product meets user needs, solves their problems, and aligns with their expectations, answering the question: “Are users willing to use and accept this product?”
2. Test Participants
- Usability Testing: Typically involves a representative group of users testing a prototype or a nearly completed product.
- User Testing: Focuses on potential or existing users, usually surveyed before the product is officially developed.
3. Implementation Stage
- Usability Testing: Usually takes place after the design phase, when a prototype or early version of the product is available for testing and usability issue fixes. However, it can also be conducted during design, development, or after launch to enhance the user experience.
- User Testing: Conducted early in the product lifecycle to validate ideas, understand user needs, and gather feedback on potential features.
4. Testing Methods
- Usability Testing: Uses tools such as First Click Tests, Session Recordings, Eye Tracking, Prototype Testing, and direct observation to identify interface issues and optimize the user experience.
- User Testing: Focuses on collecting data through User Interviews, Contextual Inquiry, and User Surveys to understand user expectations and validate product ideas
3 Common Types of Usability Testing
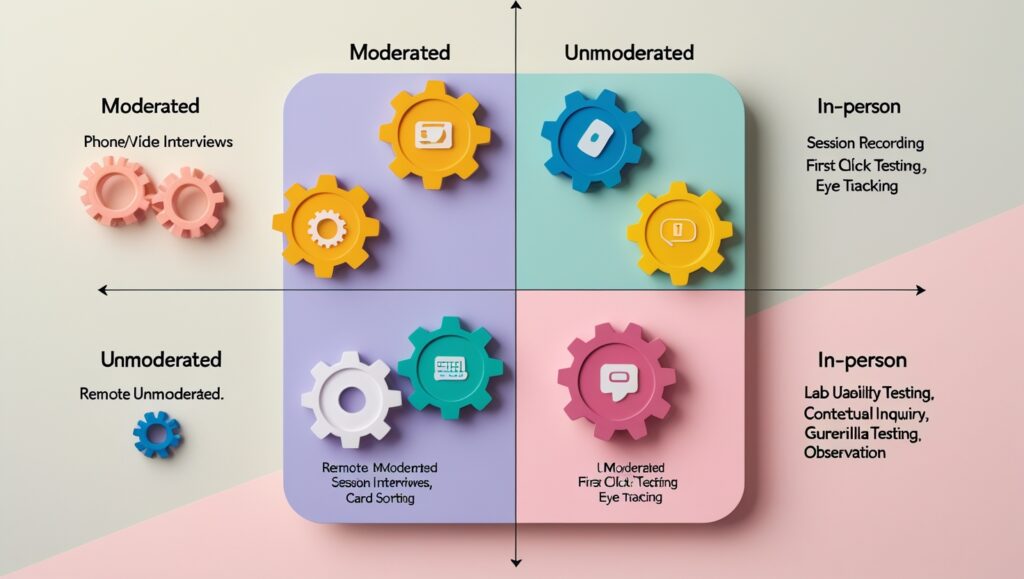
Usability Testing can be classified based on various criteria, with each method offering unique benefits. Businesses can choose the most suitable approach depending on their research objectives and available resources. Below are the most common types:
1. Qualitative vs quantitative testing
Based on the type of data collected, Usability Testing can be divided into:
- Qualitative Testing: Focuses on exploring the reasons behind user behavior. This method collects detailed feedback on user actions and feelings when interacting with the product. The goal is to identify pain points, motivations, and hidden needs—factors that numerical data alone cannot fully capture.
- Quantitative Testing: Evaluates usability by measuring specific metrics, such as task completion rate, interaction time, number of clicks, etc. This approach provides an objective assessment of usability performance while tracking improvements over different stages.
2. Moderated vs unmoderated testing
Based on the level of moderator involvement, Usability Testing can be divided into:
- Moderated Testing: Conducted with direct involvement from a moderator who guides, observes, and asks questions to clarify user behavior. This method helps gather in-depth feedback and is suitable for early design stages when a deeper understanding of the user experience is needed.
- Unmoderated Testing: Users complete tasks on their own without direct supervision. They receive instructions beforehand, while behavioral and performance data are recorded for later analysis.
3. Remote vs in-person testing
Based on the testing location, Usability Testing can be divided into:
- Remote Testing: Participants and moderators do not need to be in the same location. This method can be conducted in either moderated or unmoderated formats, allowing for a wider testing audience and cost savings. However, challenges such as network issues or difficulty in observing body language may impact the quality of collected data.
- In-person Testing: Conducted at the same location, allowing moderators to visually observe non-verbal reactions such as facial expressions, hand gestures, and user attitudes. This approach provides more detailed data but is more costly and geographically limited.
Usability Testing Process
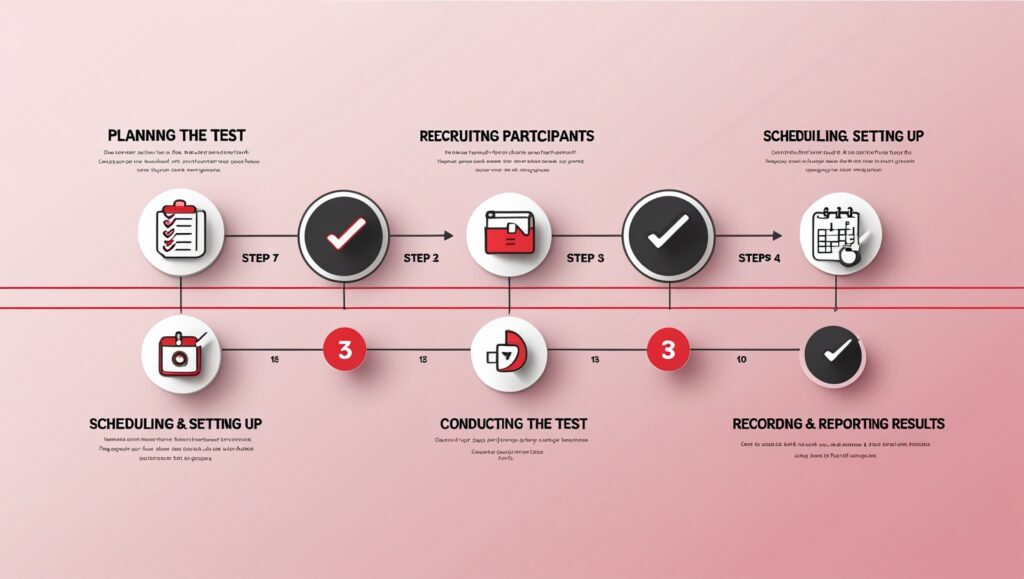
The Usability Testing process helps identify pain points and optimize the user experience by observing real user behavior. To ensure effective testing, the following steps should be followed:
1. Create a Testing Plan
The first step is to develop a detailed plan that guides the entire process. An effective plan typically includes:
- Testing objectives & scope: Clearly define the product to be evaluated, key aspects to assess, and the testing context.
- Evaluation criteria: Establish measurable indicators for usability, efficiency, and user experience.
- Participants & sample size: Identify the representative user group and determine the required sample size.
- Testing methods & tools: Choose the testing approach (moderated/unmoderated, remote/in-person) and select appropriate supporting tools.
- Test scenarios & tasks: Develop real-world tasks for users to complete, along with follow-up questions.
- Roles & responsibilities: Assign tasks to relevant stakeholders (researchers, observers, moderators).
- Timeline & execution plan: Define key milestones and expected completion time.
- Expected outcomes: Outline deliverables such as usability reports, user behavior analysis, and improvement recommendations.
A well-structured plan ensures alignment among stakeholders, optimizes the process, and delivers meaningful improvements.
See more: How to Create an Effective Usability Testing Plan? (Article in English)
2. Recruit Suitable Participants
To collect accurate insights, finding the right test participants is a key factor. After completing the planning phase, the team will identify and recruit participants based on predefined criteria. Some common methods include:
- Using recruitment tools: Platforms like Optimal Workshop and User Interviews help find suitable candidates based on specific criteria.
- Leveraging existing customers: Inviting real users of the product to participate in testing ensures authentic feedback.
- Utilizing social media & communities: Posting in relevant groups or running ads to attract suitable participants.
Selecting the right participants ensures that test results accurately reflect real user experiences, leading to meaningful product improvements.
3. Schedule & set up the testing sessions
After selecting participants, the next step is to organize and prepare the testing sessions to ensure a smooth process. Key steps include:
- Choose a suitable time: Coordinate with participants to schedule a convenient testing session, ensuring they can fully attend and are prepared.
- Send invitations & instructions: Provide detailed information about the session, including time, platform (if testing remotely), and any necessary preparations.
- Set up the testing environment: Prepare the physical or online space, ensuring all necessary tools and equipment are ready for a seamless experience.
- Conduct a trial run: Test all devices, recording tools, and testing scripts beforehand to avoid technical issues.
- Assign roles: Define specific tasks for each team member, including the facilitator, observer, and note-taker.
Careful scheduling and setup help ensure that the testing sessions run smoothly, allowing participants to focus on tasks and provide valuable feedback.
4. Conducting the Testing
When all preparations are complete, the next step is to conduct the testing session effectively. This process includes:
Provide clear instructions: Introduce the purpose of the testing session to participants, ensuring they understand that the goal is to evaluate the product, not their abilities. Avoid giving hints or guiding them through specific actions—let participants interact freely.
Observe user behavior: Monitor their task execution, noting any signs of confusion, hesitation, or errors to identify pain points.
Ask follow-up questions: After each task, ask clarifying questions such as, “What were you trying to do?” or “What were you thinking while performing this step?” This helps uncover gaps between user expectations and actual experience.
Conducting effective usability testing requires keen observation, active listening, and creating a comfortable environment where participants can openly share their thoughts.
5. Document and Report Results
After completing the testing sessions, the final step is to compile and analyze the collected data to create a Deliverable Package and share it with stakeholders to improve the product. This package typically includes:
- Session recordings: Capturing on-screen interactions, facial expressions (if applicable), and verbal feedback.
- Participant data: Including demographic information, user personas, and usage context.
- Usability Testing Report: Summarizing key findings, such as pain points, task completion rates, satisfaction levels, and important trends. Visual tools like heatmaps or task flow charts help highlight user challenges.
Detailed documentation and reporting provide actionable improvement suggestions, guiding the next steps in optimizing the user experience.
See also: What is Heuristic Evaluation? The Difference Between Heuristic and Usability Testing.
When Should Usability Testing Be Conducted?
Usability Testing is an essential part of the product lifecycle, ensuring that the product effectively meets user needs and delivers a seamless experience. Below are three key stages where usability testing is most effective:
1. Before the Development Phase
When the wireframe or prototype is ready, testing helps evaluate how users interact with the layout, structure, and functionality of the product. This allows UI/UX designers to identify navigation issues, inconsistencies in the user flow, or design flaws and make timely adjustments before the business invests resources in product development.
2. Before launching the product
Before the product is officially launched on the market, testing helps assess its effectiveness and readiness. Methods such as Task Analysis or A/B Testing evaluate how efficiently users perform key tasks, ensuring the product is ready for widespread deployment.
3. Periodically After Launch
Even after the product has been launched, periodic testing remains essential to identify new issues, adapt to changes in user behavior, and continuously improve the product over time. This process helps ensure that the product stays relevant to user needs and maintains a competitive edge in the market.
Opportunity to Receive a Free UX Audit Package at the Beginning of 2025!
Are you concerned about the user experience (UX) of your product? Don’t miss the opportunity to receive a free product audit from through the WinAudit campaign!
Through this campaign, will evaluate your product based on Heuristic Usability principles, combined with Design Principles, to identify bottlenecks that impact user experience. This is your chance to enhance your product and get ready for a breakthrough in 2025!
Note: Limited slots available! Register for WinAudit now!
Conclusion
In this article, we have shared a comprehensive guide on Usability Testing – a crucial process that helps identify and resolve issues that may impact user experience. Even if your digital product is performing well, unexpected challenges can always arise! That’s why regular testing is the key to ensuring a smooth and user-friendly experience.
If you’re looking for a professional UX testing service to enhance your digital product’s quality! We take pride in being a leading UI/UX design studio, specializing in UX research, design, and product development across multiple digital platforms.
Contact us today to schedule a FREE consultation and discover how we can apply usability testing standards to optimize the user experience for your product!