click to get service View profile
In a world where artificial intelligence is shaping how we work, shop, communicate, and even think — the biggest challenge isn’t just making AI smarter, it’s making it more human. That’s where AI Design Thinking comes in.
AI Design Thinking is the intersection of powerful algorithms and deep human empathy. It blends the structured problem-solving mindset of design thinking with the innovation potential of AI — helping teams build solutions that are not only intelligent, but also ethical, useful, and emotionally aware.
In this guide, we’ll break down how to apply design thinking principles to your AI projects — from understanding real user needs to designing thoughtful, transparent, and responsible AI products.
Whether you’re a designer, developer, or product strategist, this article will show you how to shift from just building smart tech to creating meaningful, human-centered experiences with AI.
What is Design Thinking?
AI Design Thinking is a human-centered, iterative approach that empowers teams to solve complex problems by combining empathy, creativity, and rapid experimentation. It encourages a deep understanding of real user needs, challenges existing assumptions, and promotes the development of innovative AI solutions that can be quickly tested, validated, and improved.
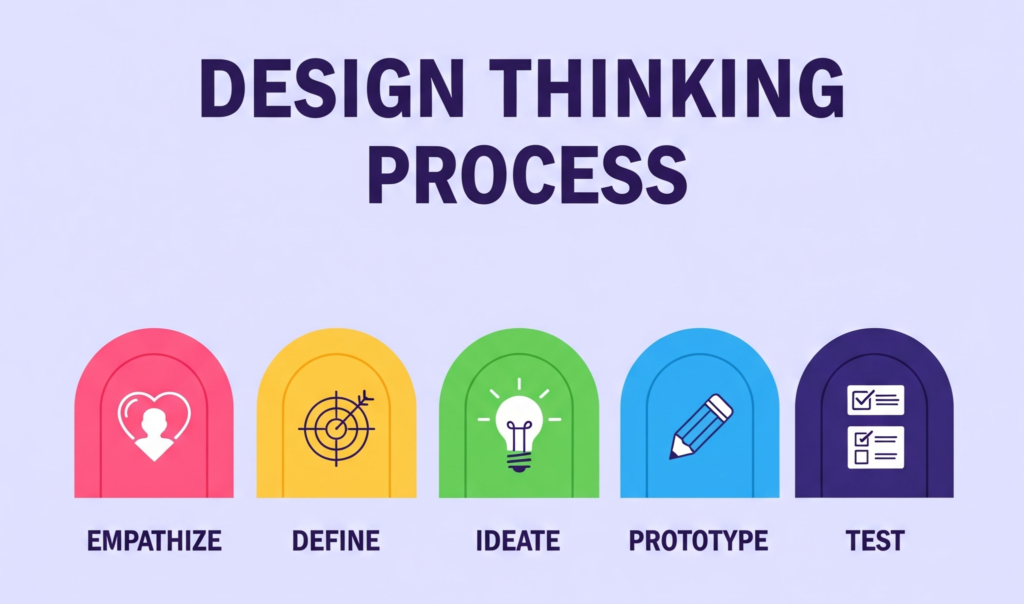
This approach is particularly effective when the problem is not clearly defined, requiring a deep exploration of user behaviors and motivations. The process is commonly organized into five key stages:
- Empathize: Design teams observe and engage with users to understand their needs, emotions, and experiences. Rather than guessing, designers seek to uncover real challenges by listening and learning from people.
- Define: Designers synthesize what they’ve learned into a clear, focused problem statement. This phase turns observations into actionable insights, framing the design challenge around the user’s core need.
- Ideate: Design teams generate a wide range of ideas to solve the problem. The focus is on exploring freely, encouraging bold or unexpected concepts without immediate judgment.
- Prototype: Design teams develop simple, early versions of solutions to see how they might work in practice. These prototypes, whether sketches, models, or digital mockups, help visualize the concept and gather early reactions.
- Test: Designers present these prototypes to real users, observe how they interact with them, and collect feedback. This stage is key for learning what works, what doesn’t, and how to improve, often through multiple rounds of changes.
What is AI Design Thinking?
AI design thinking is the integration of artificial intelligence into the traditional, human-centered design thinking process. It combines the strengths of both—AI’s ability to process vast amounts of data quickly, and human designers’ empathy, intuition, and creativity. The goal isn’t to replace people with machines, but to amplify what teams can achieve by working alongside intelligent tools.
When applied intentionally, AI becomes a valuable partner in the AI Design Thinking process—uncovering patterns, generating ideas, and accelerating testing. It enhances research, streamlines prototyping, and supports better decision-making, making design thinking more agile, efficient, and scalable for modern innovation.
The following sections explore the key benefits of using AI in design thinking, as well as the challenges that teams need to navigate to use it effectively and responsibly.
Benefits of Integrating AI into the Design Thinking Process
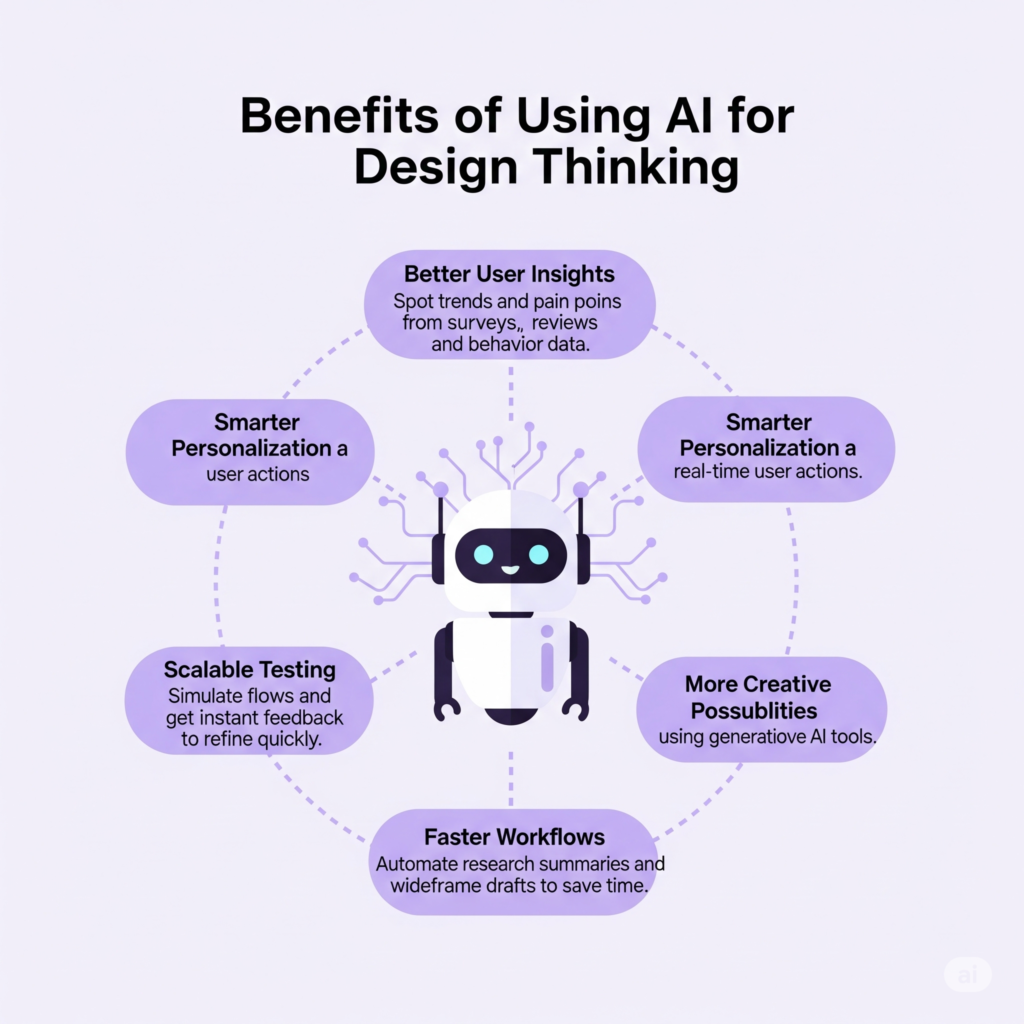
Adding AI to design thinking brings powerful advantages across the entire process. Here’s how it helps:
1. Better User Insights
In the AI Design Thinking process, AI can efficiently analyze large volumes of data—such as surveys, reviews, and social media—to reveal trends, user behaviors, and pain points. Tools powered by natural language processing (NLP) can interpret text-based feedback and uncover key insights that might be missed by human researchers, enabling more informed and user-centered design decisions.
2. Faster Workflows
AI can automate routine design tasks such as sorting research data, summarizing user responses, or producing initial wireframe drafts. This not only accelerates workflows but also frees up teams to spend more time on ideation and problem-solving.
3. Smarter Personalization
AI enables hyper-personalization by analyzing user behavior patterns, such as browsing history, clicks, or time spent on features. The AI uses these insights to automatically adjust content, interfaces, or functionality for different users. This helps deliver more relevant, meaningful experiences tailored to each user’s needs and preferences.
4. More Creative Possibilities
AI Design Thinking enhances creativity by enabling teams to generate diverse ideas and design variations beyond conventional approaches. Tools like ChatGPT and Midjourney support brainstorming and prototyping by rapidly producing concepts, themes, and visuals. This accelerates the creative process and allows teams to explore a wider range of possibilities in less time.
5. Scalable Testing
AI can simulate hundreds of users interacting with your design, helping you test multiple ideas quickly before involving real people. AI tools can also monitor real user testing sessions and provide instant feedback about usability issues and suggested fixes.
Challenges of Using AI for Design Thinking
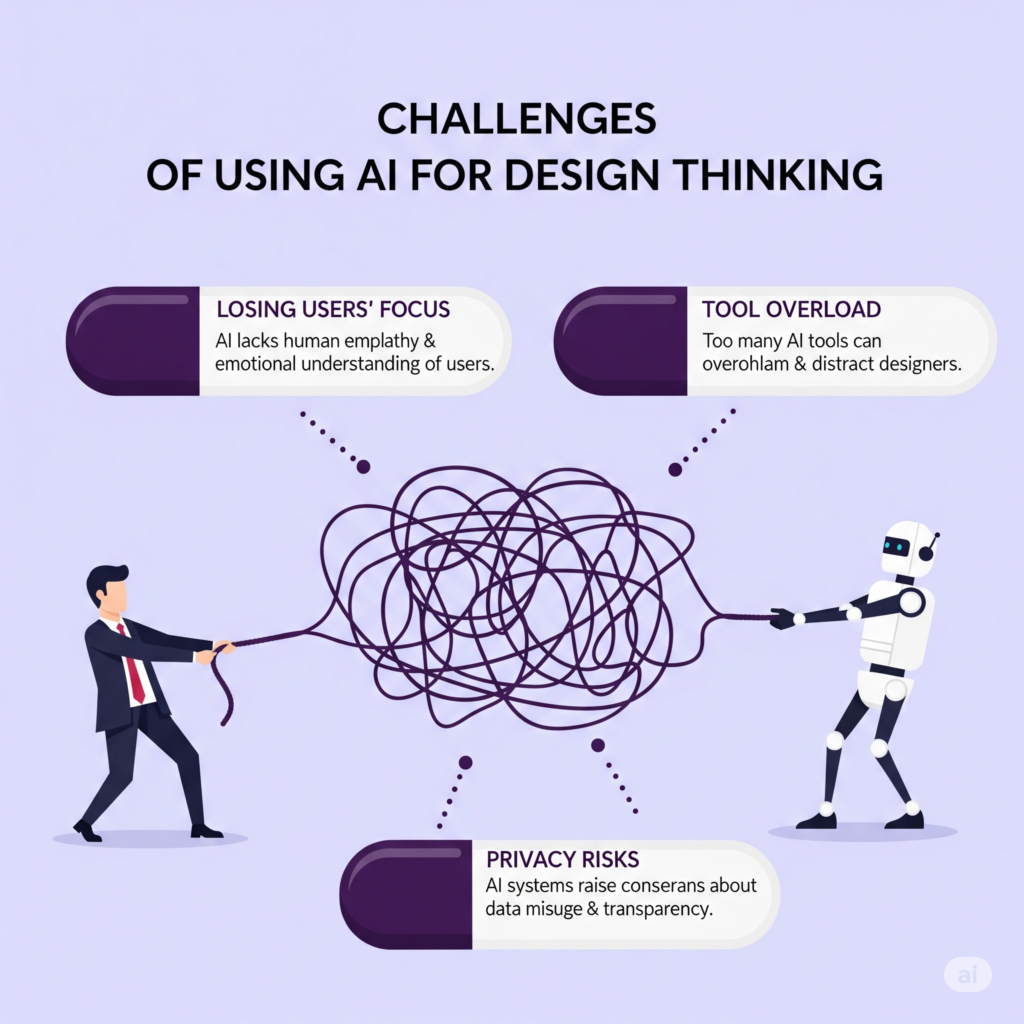
While AI can boost speed and insight in the design process, it also introduces new risks. To use AI responsibly and effectively in design thinking, here are the key challenges teams must consider:
1. Losing Users’ Focus
AI can analyze user behavior patterns, but it cannot understand human emotions like frustration, excitement, or confusion. Teams may rely too heavily on AI data instead of talking directly to users. This creates designs that solve surface problems but miss deeper emotional needs.
Tip: Use AI insights as a starting point, but always validate findings through direct user interviews and observations.
2. Tool Overload
In the context of AI Design Thinking, the rapid growth of AI tools can overwhelm teams with endless choices. Instead of focusing on solving user problems, teams may find themselves stuck learning new platforms or chasing the latest trends. This distraction often leads to fragmented workflows, reduced productivity, and burnout—making it crucial to adopt a thoughtful, purpose-driven approach when integrating AI into the design process.
Tip: Start with one or two AI tools that address your biggest pain points, and master them before adding new ones to your workflow.
3. Privacy Risks
AI tools often require large amounts of user data to work effectively, creating privacy and security concerns. Teams may collect personal information without users fully understanding how it’s being used. Poor data handling can damage user trust and create legal problems.
Tip: Always be transparent about data collection, get clear user consent, and regularly audit your data practices to ensure compliance.
How Does AI-Enhanced Design Thinking?
AI Design Thinking integrates artificial intelligence across every phase of the design process—from gathering insights and identifying patterns to generating ideas and testing solutions. Rather than replacing the human touch, AI acts as a force multiplier, enhancing speed, creativity, and exploration while keeping the process rooted in real user needs. It empowers teams to move faster and think broader without losing sight of what truly matters: designing for people.
Let’s take a closer look at how AI supports each phase:
1. AI in Empathy
Understanding users is central to design thinking, but gathering meaningful insights from user interviews, feedback, and surveys can be a time-consuming process.
Designers often spend extensive time observing users, conducting one-on-one conversations, and analyzing qualitative data to gain a deeper understanding of their needs, emotions, and pain points. While this approach is valuable, it can be overwhelming due to the sheer volume of data and the slow pace of manual analysis.
Here’s how AI supports empathy-driven design:
- Spotting emotions at scale: AI leverages sentiment analysis and natural language processing (NLP) to process large volumes of reviews, surveys, or transcripts. This helps identify common emotions and pain points across user feedback.
- Tracking user behavior: AI-powered behavioral analytics track user interactions, such as clicks, scrolls, and drop-offs. These insights pinpoint areas where users encounter difficulties or disengage.
- Gathering insights via chatbots: Conversational AI collects real-time user feedback through automated chats. This allows teams to gather continuous input with minimal manual effort.
2. AI in Definition
In the AI Design Thinking process, once user data is collected, teams must organize and interpret it to uncover valuable insights. This phase involves synthesizing information, identifying core user needs, and crafting clear problem statements to guide ideation. While essential, it can be a messy and complex stage where critical details are easily missed—making structure, clarity, and the right tools especially important.
Designers spend time organizing data on whiteboards or digital tools, looking for patterns and grouping similar feedback. Designers must carefully sort through feedback to tell apart surface complaints from deeper user needs. Without a clear structure, it’s easy to misinterpret the data, rush into solutions, or miss the real problems entirely.
AI supports this phase by:
- Spotting common patterns: AI uses clustering and pattern recognition to group similar user comments or behaviors. This helps teams easily detect frequently mentioned issues or shared user frustrations.
- Extracting key themes: Automated synthesis tools scan interview transcripts or survey data to highlight recurring user goals, emotional drivers, and problem areas that matter most.
- Forecasting future needs: Predictive modeling analyzes user data trends to anticipate upcoming expectations or shifts in behavior. This helps teams define more forward-thinking problem statements.
3. AI in Ideation and Prototyping
Ideation and prototyping are the phases where teams generate potential solutions and shape them into visuals through sketches, wireframes, or early mockups.
Designers lead brainstorming sessions, explore creative directions, and build quick prototypes to validate ideas before investing in development. However, when teams are under tight deadlines, they may skip exploration or settle on familiar ideas, thereby limiting creativity and innovation.
AI supports this phase by:
- Generating and visualizing ideas faster: Generative AI tools like ChatGPT or DALL·E help teams quickly explore different design ideas and turn them into visuals. From a simple prompt, they can suggest multiple solutions and instantly turn them into images like mockups or mood boards—speeding up both creativity and concept development.
- Building prototypes faster: AI-assisted platforms like Uizard or Figma AI can transform written prompts or rough hand-drawn ideas into interactive wireframes. This helps teams move from concept to testable prototype with much less manual work.
- Simulating user reactions early: AI tools like Maze or UserZoom let teams preview how users might behave with a design, even before real testing starts. This helps catch major issues early, like confusing layouts or unclear buttons, so teams can fix them before investing in full usability tests.
4. AI in Testing
In the AI Design Thinking process, testing is essential for validating whether a solution truly meets user needs. It helps uncover points of friction, confusion, or unmet expectations. During this phase, teams define clear test objectives, conduct usability sessions, and analyze results to guide design improvements. However, evaluating feedback at scale and comparing multiple design iterations can be time-consuming and susceptible to bias—highlighting the need for intelligent, data-driven support.
AI supports this phase by:
- Running smarter A/B tests: Platforms such as Google Optimize or Adobe Target use AI to test multiple design variations in real time. They automatically highlight the top-performing version based on actual user behavior.
- Making feedback actionable: After usability tests or product launches, teams often collect open-ended comments from users. AI tools help sort through this feedback at scale, pinpointing specific pain points or recurring issues that testers mention, so teams know exactly what to improve next.
- Real-time analytics: AI can monitor how users navigate a prototype, such as where they click, how long they hesitate, or what they say during a usability test. This real-time analysis helps teams immediately identify confusing steps or unclear content and adjust the design on the spot.
Final Thoughts
As artificial intelligence continues to shape our world, the need for human-centered solutions has never been greater. By integrating AI Design Thinking, we’re not just building smarter machines — we’re designing experiences that respect, understand, and serve real human needs.
AI Design Thinking empowers teams to move beyond just algorithms and data, placing greater emphasis on empathy, ethics, and usability. Whether you’re building a chatbot, a recommendation engine, or a full-scale AI platform, this approach ensures your solutions are not only intelligent but also meaningful, responsible, and centered around real human needs.
In the end, great AI isn’t just about what it can do. It’s about who it’s for — and how thoughtfully it’s designed.